Layer 3
Invaluable Inclusion to Your Network
Oct 21, 2022
Invaluable Inclusion to Your Network
Taipei, Taiwan, Oct 21, 2022—Numerous high-speed data networks are built using industrial network switches. These switches are utilized to link different devices in a network and are thus a crucial need. The Open System Interconnect (OSI) model defines network communications. This model has seven layers: Application Layer, Presentation Layer, Session Layer, Transport Layer, Network Layer, Data Link Layer, and Physical Layer. The layer 3 switch operates on the network layer. As convergent networks grow in size and data network density grows, so does the demand for layer 3 switches. Layer 3 switches were developed to enhance network routing performance on big local area networks such as corporate intranets. If only Layer 2 switching is used in a big corporate intranet, the MAC tables must be quite extensive to keep track of where each packet should be moved to. The larger the intranets, the more dangerous and congested the network got.
Many systems in today's complex business networks with several subnets require a layer 3 switch. A layer 3 switch, in simplest terms, combines the functions of a switch and a router. It may operate as a switch to connect devices on the same subnet or virtual LAN at lightning speeds, as well as a router because it contains IP routing intelligence. It can handle routing protocols, analyze incoming packets, and make routing decisions based on source and destination addresses. A layer 3 switch works as both a switch and a router in this manner. A layer 3 switch, also known as a multilayer switch, adds a tremendous amount of flexibility to a network. Compared to layer 2 switches, layer 3 switches switch at a quicker rate. They are even faster than typical routers since they route data packets without the need for extra hops, resulting in increased performance. Due to the efficacy of this routing strategy in Layer 3 switches, they are utilized for network construction of inter and intra networks. Since packets do not have to pass via a router in addition, Layer 3 switches are less prone to face network latency.
Scalability, security, and Quality of Service (QoS) may all be offered by Layer 3 switches, along for logical sub-network segmentation. QoS adds bandwidth reserve and packet delay constraints to th fundamental packet priority found in the Class of Service (CoS). Depending on the target IP address, packets in a Layer 3 system are routed to a certain next-hop IP address. Unlike MAC addresses on a Layer 2 switch, IP addresses on a Layer 3 switch are included in each IP packet. The Internet's backbone, as well as the backbones of many major corporations, are built on a Layer 3 foundation. Increased power and security are other features found in Layer 3 switches. Considering that these switches are typically placed at the center of a network, they need to be able to withstand extremely high traffic loads. In addition, some Layer 3 switches include 10 Gigabit SFP+ ports for high-capacity inter-switch connectivity.
Layer 3 switches often have some of the most complete security of any switch. These switches can function in environments where total security is required, thanks to features like 802.1x authentication, loopback detection, and ARP inspection. If a network has thousands of users of the network infrastructure requires heavy device management for the roll-out of patching or policy updates, or if specific control rules must be activated on specific devices within the network, a layer 3 switch is more appropriate due to its firewall protections. The most important function of a Layer 3 switch is to accelerate data forwarding within a large local area network, and the addition of routing services serves this aim. Assume a large network is separated into tiny LANs based on departments, regions, and other criteria. In that instance, there will be a huge number of inter-network accesses, and the mere usage of Layer 2 switches will not be sufficient.
Due to the restricted number of interfaces and sluggish routing and forwarding speed of routers, for example, limiting network speed and network size, the usage of fast-forwarding Layer 3 switches with routing function becomes the preferred choice. Given that separate locations, intersections, or types of data (video, image, and signals) must be partitioned, Layer 3 switches are most frequently employed to support routing between VLANs. The layer 3 switch is extremely simple to use. Its primary function is to replace the traditional router as the networks's core. As a result, if there is no requirement for a WAN connection but a router is necessary, the layer 3 switch can be utilized instead. Layer 3 switches are commonly used in the core layer of corporate and campus networks, and the Gigabit port or 100 megabytes port on layer 3 switches is used to link multiple subnets or VLANs. This result in a network layout that is very straightforward and has a minimal number of nodes. It also means that fewer control functions are requires, which lowers the communications.
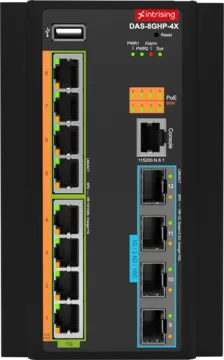
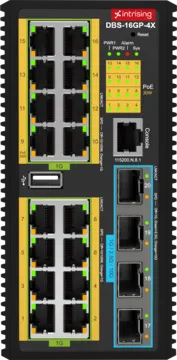
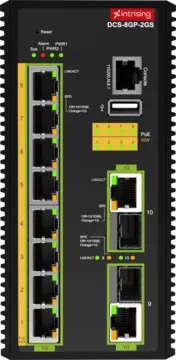
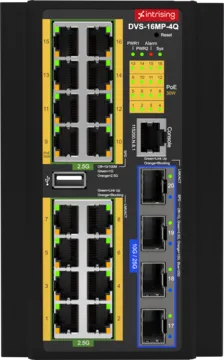
Intrising Layer 3 Industrial Switches are reliable and high-performance. We have D Series Industrial Switches which will be a perfect option as it comes with a various number of ports that you can choose according to your needs and preferences. DAS-8GHP-4X, DBS-16GP-4X, DCS-8GP-2GS, and DVS-16MP-4Q are some of our D Series Layer 3 Industrial Switches that you can pick for your network.